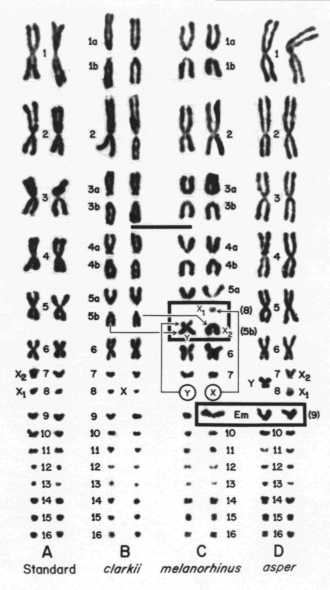

Figure 5. Karyotypic relationships of the clarki group species. A. The standard crevice user karyotype, represented by S. mucronatus ♀ (Mexico: Veracruz; 8 km ESE Las Vigas) . B. The S. clarki ♀ karyotype (my material does not include good male mitoses--Mexico: Sinaloa; 6 km NNW Mazatlan). C. The S. melanorhinus ♂ karyotype, heterozygous for the Em chromosome (Mexico: Colima; 10 km E Manzanillo). D. The S. asper ♂ karyotype, fixed for the Em chromosome (same individual used in Fig. 4). The scale bar in the center of the figure represents 10 Ám. Em chromosomes and the sex chromosomes of melanorhinus are inclosed in boxes. The long arm of the melanorhinus neo-Y clearly derives from one of the acrocentric fission products of the standard pair 5, which is fused to the "y" [terminology of Table 1] of clarki--which in turn probably corresponds to the long arm of the "y," chromosome of the standard-crevice user karyotype shown in the adjacent asper karyotype. The x [or X chromosome of Table 1] is the un-fused homolog of the long arm of the melanorhinus neo-Y. The meiotic pairing of these chromosomes is shown in Fig. 6.